RESEARCH ARTICLE
New Distances to Four Supernova Remnants
S. Ranasinghe1, D. A. Leahy1, *, Wenwu Tian1, 2
Article Information
Identifiers and Pagination:
Year: 2018Volume: 4
First Page: 1
Last Page: 13
Publisher Id: PHY-4-1
DOI: 10.2174/1874843001804010001
Article History:
Received Date: 9/3/2018Revision Received Date: 20/05/2018
Acceptance Date: 01/06/2018
Electronic publication date: 29/06/2018
Collection year: 2018
open-access license: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC-BY 4.0), a copy of which is available at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
Object:
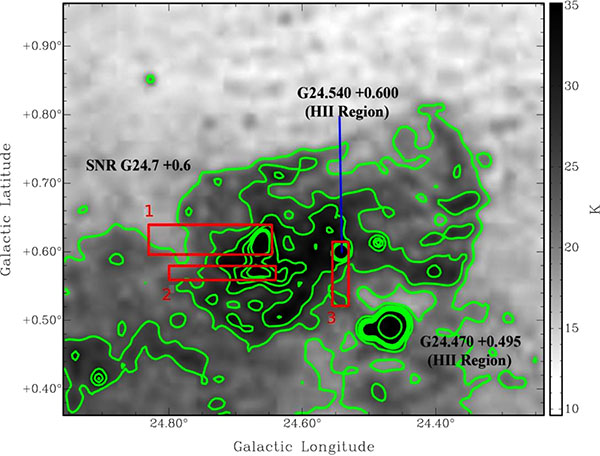
Distances are found for four supernova remnants without previous distance measurements. H I spectra and H I channel maps are used to determine the maximum velocity of H I absorption for the four Supernova Remnants (SNRs).
Method:
We examined 13CO emission spectra and channel maps to look for possible molecular gas associated with each SNR, but did not find any.
Result:
The resulting distances for the SNRs are 3.5 ± 0.2 kpc (G24.7+0.6), 4.7 ± 0.3 kpc (G29.6+0.1), 4.1 ± 0.5 kpc (G41.5+0.4) and 4.5 ± 0 .4 - 9.0 ± 0.4 kpc (G57.2+0.8).